Mitwirkende Plattenbreite (Bsp.): Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
| (42 dazwischenliegende Versionen von 3 Benutzern werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
==Beispiel 1 <small>Stahlbeton-Plattenbalken mit Kragarm</small>== | ==Beispiel 1 <small>Stahlbeton-Plattenbalken mit Kragarm</small>== | ||
| + | Das folgende Beispiel zeigt eine Berechnung der [[Zusatzangaben Plattenbalken (S340.de)#Berechnungsgrundlagen für die Ermittlung der mitwirkenden Plattenbreite|mitwirkenden Plattenbreite]], wie Sie mit dem Modul S340.de geführt wird. | ||
=== Aufgabe === | === Aufgabe === | ||
Ermittlung der mitwirkenden Plattenbreite eines Plattenbalkens am Randbereich:<br /> | Ermittlung der mitwirkenden Plattenbreite eines Plattenbalkens am Randbereich:<br /> | ||
| Zeile 14: | Zeile 18: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
==== Vorgabewerte ==== | ==== Vorgabewerte ==== | ||
| − | Die Ermittlung der [[Effektive Stützweiten ( | + | Die Ermittlung der [[Effektive Stützweiten (S***.de)|effektiven Stützweiten]] erfolgte nach Regeln des Moduls S340.de<br /> |
| − | + | <br /> | |
| − | <math>l_{eff,1}=</math> | + | <math>l_\mathrm{eff,1}=400\,\mathrm{cm}</math><br /><br /> |
| − | <math>l_{eff,Kr}=</math> | + | <math>l_\mathrm{eff,Kr}=150\,\mathrm{cm}</math><br /> |
=== Berechnung === | === Berechnung === | ||
==== wirksame Stützweiten ==== | ==== wirksame Stützweiten ==== | ||
| − | <math>l_{0,1}=0,85 | + | <br /> |
| − | <math>l_{0,Kr}=1,5 | + | <math>l_\mathrm{0,1}=0{,}85 \cdot l_\mathrm{eff,1}=0{,}85 \cdot 400\,\mathrm{cm} = \underline{340\,\mathrm{cm}} </math><br /><br /> |
| + | <math>l_\mathrm{0,Kr}=1{,}5 \cdot l_\mathrm{eff,Kr}=1{,}5 \cdot 150\,\mathrm{cm} = \underline{225\,\mathrm{cm}} </math><br /> | ||
| + | |||
==== Feld 1 ==== | ==== Feld 1 ==== | ||
| − | <math>b_{eff}=b_{eff,1}+b_{eff, | + | <br /> |
| − | <math>b_{w}=</math> | + | <math>b_\mathrm{eff}=b_\mathrm{eff,1} + b_\mathrm{eff,2} + b_\mathrm{w}~</math><br /> |
| − | <math>b_{eff,1}=min\begin{cases} | + | <br /> |
| − | 0,2 | + | <math>b_\mathrm{w}=20\,\mathrm{cm}</math><br /> |
| − | 0,2 | + | <br /> |
| − | b_{ | + | <math>b_\mathrm{eff,1}=\mathrm{min}\begin{cases} |
| − | \end{cases}</math> | + | 0{,}2 \cdot 30\,\mathrm{cm} + 0{,}1 \cdot 340\,\mathrm{cm} &= 40\,\mathrm{cm} \\ |
| + | 0{,}2 \cdot 340\,\mathrm{cm} &= 68\,\mathrm{cm} \\ | ||
| + | b_\mathrm{1} &= \underline{30\,\mathrm{cm}} | ||
| + | \end{cases}</math><br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <math>b_\mathrm{eff,2}=\mathrm{min}\begin{cases} | ||
| + | 0{,}2 \cdot 150\,\mathrm{cm} + 0{,}1 \cdot 340\,\mathrm{cm} &= \underline{64\,\mathrm{cm}} \\ | ||
| + | 0{,}2 \cdot 340\,\mathrm{cm} &= 68\,\mathrm{cm} \\ | ||
| + | b_\mathrm{2} &= 150\,\mathrm{cm} | ||
| + | \end{cases}</math><br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <math>b_\mathrm{eff}=30\,\mathrm{cm} + 64\,\mathrm{cm} + 20\,\mathrm{cm}= \underline{\underline{114\,\mathrm{cm}}}</math><br /> | ||
| − | ==== | + | ==== Kragarm ==== |
| − | <math> | + | <br /> |
| − | <math> | + | <math>b_\mathrm{eff}=b_\mathrm{eff,1} + b_\mathrm{eff,2} + b_\mathrm{w}~</math><br /> |
| − | + | <br /> | |
| − | <math> | + | <math>b_\mathrm{w}=20\,\mathrm{cm}</math><br /> |
| − | + | <br /> | |
| − | <math> | + | <math>b_\mathrm{eff,1}=\mathrm{min}\begin{cases} |
| − | + | 0{,}2 \cdot 30\,\mathrm{cm} + 0{,}1 \cdot 225\,\mathrm{cm} &= \underline{28{,}5\,\mathrm{cm}} \\ | |
| − | <math> | + | 0{,}2 \cdot 225\,\mathrm{cm} &= 45\,\mathrm{cm} \\ |
| − | + | b_\mathrm{1} &= 30\,\mathrm{cm} | |
| + | \end{cases}</math><br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <math>b_\mathrm{eff,2}=\mathrm{min}\begin{cases} | ||
| + | 0{,}2 \cdot 150\,\mathrm{cm} + 0{,}1 \cdot 225\,\mathrm{cm} &= 52{,}5\,\mathrm{cm} \\ | ||
| + | 0{,}2 \cdot 225\,\mathrm{cm} &= \underline{45\,\mathrm{cm}} \\ | ||
| + | b_\mathrm{2} &= 150\,\mathrm{cm} | ||
| + | \end{cases}</math><br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <math>b_\mathrm{eff}=28{,}5\,\mathrm{cm} + 45\,\mathrm{cm} + 20\,\mathrm{cm}= \underline{\underline{93{,}5\,\mathrm{cm}}}</math><br /> | ||
=== Vergleich mit mb-AEC Baustatik === | === Vergleich mit mb-AEC Baustatik === | ||
| − | Bei | + | Bei Ermittlung der mitwirkenden Plattenbreite erscheint folgender Ausdruck:<br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Mitwirkende Plattenbreite (Bsp.) 3.png|rahmenlos|rand|tumb|800px|Ausdruck vom Modul S340.de]] |
| + | |||
==Quellen== | ==Quellen== | ||
| − | == | + | {{Seiteninfo(mb) |
| − | + | |Quality-flag = [[File:quality-flag-orange.gif|right|70px]] | |
| − | + | |Status = Seite fertig, ungeprüft| | |
| − | + | |Modul-Version = 2014.011 | |
| − | + | }} | |
| − | [[Kategorie:Beispiele]] | + | [[Kategorie:Beispiele-Stahlbetonbau]] |
Aktuelle Version vom 11. November 2019, 17:14 Uhr
Beispiel 1 Stahlbeton-Plattenbalken mit Kragarm
Das folgende Beispiel zeigt eine Berechnung der mitwirkenden Plattenbreite, wie Sie mit dem Modul S340.de geführt wird.
Aufgabe
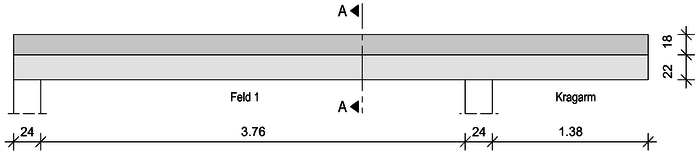
Ermittlung der mitwirkenden Plattenbreite eines Plattenbalkens am Randbereich:
Ansicht
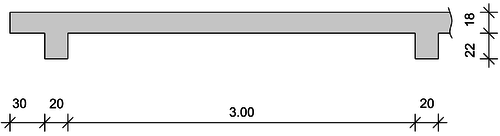
Schnitt A-A
Vorgabewerte
Die Ermittlung der effektiven Stützweiten erfolgte nach Regeln des Moduls S340.de
Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle l_\mathrm{eff,1}=400\,\mathrm{cm}}
Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle l_\mathrm{eff,Kr}=150\,\mathrm{cm}}
Berechnung
wirksame Stützweiten
Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle l_\mathrm{0,1}=0{,}85 \cdot l_\mathrm{eff,1}=0{,}85 \cdot 400\,\mathrm{cm} = \underline{340\,\mathrm{cm}} }
Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle l_\mathrm{0,Kr}=1{,}5 \cdot l_\mathrm{eff,Kr}=1{,}5 \cdot 150\,\mathrm{cm} = \underline{225\,\mathrm{cm}} }
Feld 1
Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle b_\mathrm{eff}=b_\mathrm{eff,1} + b_\mathrm{eff,2} + b_\mathrm{w}~}
Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle b_\mathrm{w}=20\,\mathrm{cm}}
Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle b_\mathrm{eff,1}=\mathrm{min}\begin{cases} 0{,}2 \cdot 30\,\mathrm{cm} + 0{,}1 \cdot 340\,\mathrm{cm} &= 40\,\mathrm{cm} \\ 0{,}2 \cdot 340\,\mathrm{cm} &= 68\,\mathrm{cm} \\ b_\mathrm{1} &= \underline{30\,\mathrm{cm}} \end{cases}}
Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle b_\mathrm{eff,2}=\mathrm{min}\begin{cases} 0{,}2 \cdot 150\,\mathrm{cm} + 0{,}1 \cdot 340\,\mathrm{cm} &= \underline{64\,\mathrm{cm}} \\ 0{,}2 \cdot 340\,\mathrm{cm} &= 68\,\mathrm{cm} \\ b_\mathrm{2} &= 150\,\mathrm{cm} \end{cases}}
Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle b_\mathrm{eff}=30\,\mathrm{cm} + 64\,\mathrm{cm} + 20\,\mathrm{cm}= \underline{\underline{114\,\mathrm{cm}}}}
Kragarm
Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle b_\mathrm{eff}=b_\mathrm{eff,1} + b_\mathrm{eff,2} + b_\mathrm{w}~}
Fehler beim Parsen (Konvertierungsfehler. Der Server („https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_“) hat berichtet: „Cannot get mml. Server problem.“): {\displaystyle b_{\mathrm {w} }=20\,\mathrm {cm} }
Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle b_\mathrm{eff,1}=\mathrm{min}\begin{cases} 0{,}2 \cdot 30\,\mathrm{cm} + 0{,}1 \cdot 225\,\mathrm{cm} &= \underline{28{,}5\,\mathrm{cm}} \\ 0{,}2 \cdot 225\,\mathrm{cm} &= 45\,\mathrm{cm} \\ b_\mathrm{1} &= 30\,\mathrm{cm} \end{cases}}
Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle b_\mathrm{eff,2}=\mathrm{min}\begin{cases} 0{,}2 \cdot 150\,\mathrm{cm} + 0{,}1 \cdot 225\,\mathrm{cm} &= 52{,}5\,\mathrm{cm} \\ 0{,}2 \cdot 225\,\mathrm{cm} &= \underline{45\,\mathrm{cm}} \\ b_\mathrm{2} &= 150\,\mathrm{cm} \end{cases}}
Fehler beim Parsen (MathML mit SVG- oder PNG-Rückgriff (empfohlen für moderne Browser und Barrierefreiheitswerkzeuge): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle b_\mathrm{eff}=28{,}5\,\mathrm{cm} + 45\,\mathrm{cm} + 20\,\mathrm{cm}= \underline{\underline{93{,}5\,\mathrm{cm}}}}
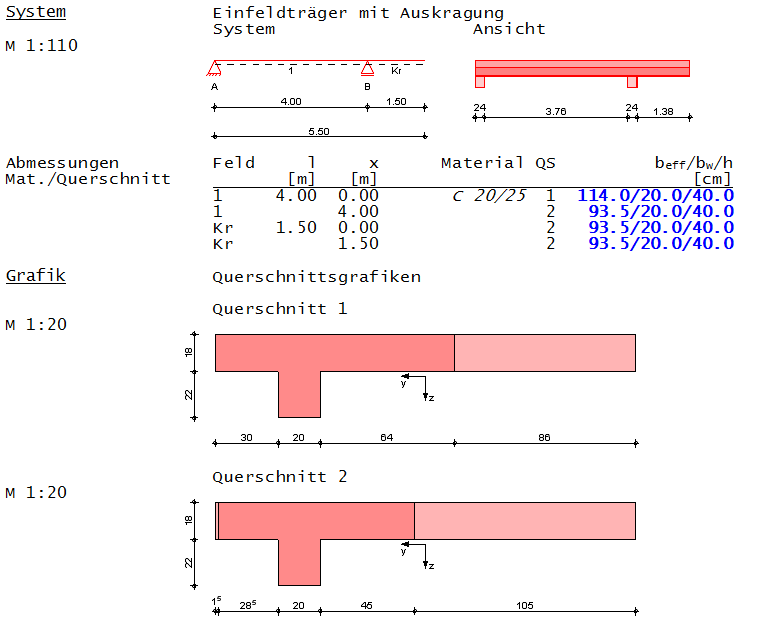
Vergleich mit mb-AEC Baustatik
Bei Ermittlung der mitwirkenden Plattenbreite erscheint folgender Ausdruck:
Quellen
Seiteninfo
|