Mitwirkende Plattenbreite (Bsp.): Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Zur Navigation springen
Zur Suche springen
(→Feld 1) |
|||
| Zeile 46: | Zeile 46: | ||
==== Kragarm ==== | ==== Kragarm ==== | ||
| − | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | <math>b_{w} | + | <math>b_\mathrm{eff}=b_\mathrm{eff,1} + b_\mathrm{eff,2} + b_\mathrm{w}</math><br /> |
| − | <math>b_{eff, | + | <br /> |
| − | 0,2 | + | <math>b_\mathrm{w}=20\,\mathrm{cm}</math><br /> |
| − | 0,2 | + | <br /> |
| − | b_{1} &= 30 cm | + | <math>b_\mathrm{eff,1}=\mathrm{min}\begin{cases} |
| + | 0{,}2 \cdot 30\,\mathrm{cm} + 0{,}1 \cdot 225\,\mathrm{cm} &= \underline{28{,}5\,\mathrm{cm}} \\ | ||
| + | 0{,}2 \cdot 225\,\mathrm{cm} &= 45\,\mathrm{cm} \\ | ||
| + | b_\mathrm{1} &= 30\,\mathrm{cm} | ||
\end{cases}</math><br /> | \end{cases}</math><br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | <math>b_{eff, | + | <math>b_\mathrm{eff,2}=\mathrm{min}\begin{cases} |
| − | 0,2 | + | 0{,}2 \cdot 150\,\mathrm{cm} + 0{,}1 \cdot 225\,\mathrm{cm} &= 52{,}5\,\mathrm{cm} \\ |
| − | 0,2 | + | 0{,}2 \cdot 225\,\mathrm{cm} &= \underline{45\,\mathrm{cm}} \\ |
| − | b_{2} &= | + | b_\mathrm{2} &= 150\,\mathrm{cm} |
\end{cases}</math><br /> | \end{cases}</math><br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | <math>b_{eff}=28,5 cm +45 cm +20 cm= | + | <math>b_\mathrm{eff}=28{,}5\,\mathrm{cm} + 45\,\mathrm{cm} + 20\,\mathrm{cm}= \underline{\underline{93{,}5\,\mathrm{cm}}}</math><br /> |
=== Vergleich mit mb-AEC Baustatik === | === Vergleich mit mb-AEC Baustatik === | ||
Version vom 2. März 2015, 10:37 Uhr
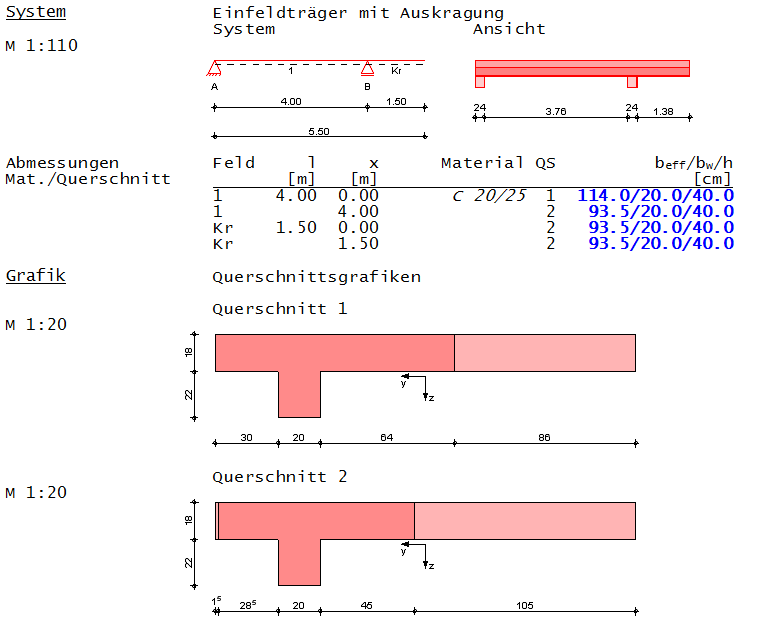
Beispiel 1 Stahlbeton-Plattenbalken mit Kragarm
Aufgabe
Ermittlung der mitwirkenden Plattenbreite eines Plattenbalkens am Randbereich:
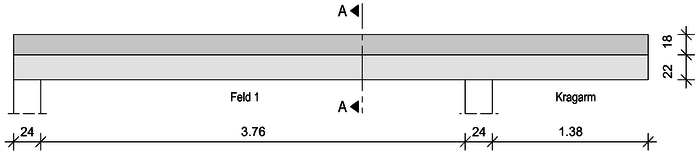
Ansicht
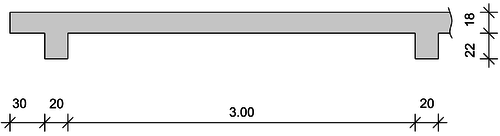
Schnitt A-A
Vorgabewerte
Die Ermittlung der effektiven Stützweiten erfolgte nach Regeln des Moduls S340.de
Berechnung
wirksame Stützweiten
Feld 1
Kragarm
Vergleich mit mb-AEC Baustatik
Bei Ermittlung der mitwirkenden Plattenbreite, erscheint folgender Ausdruck:
Quellen
Sonstiges
- Modul-Version: 2014.011
- Autor: R. Wengatz
- Veröffentlicht am: 24.02.2015
- Status: in Bearbeitung